Exercise method explanation
Description
This page explains the various motion methods on Motion86.
Motion method reference table
| Motion method |
|---|
| Linear motion |
| Arc motion |
| Circular motion |
| Spiral motion |
Linear motion:
When using the linear motion method to control the Machine , the machine will go straight to the target position, as shown in Figure 1:
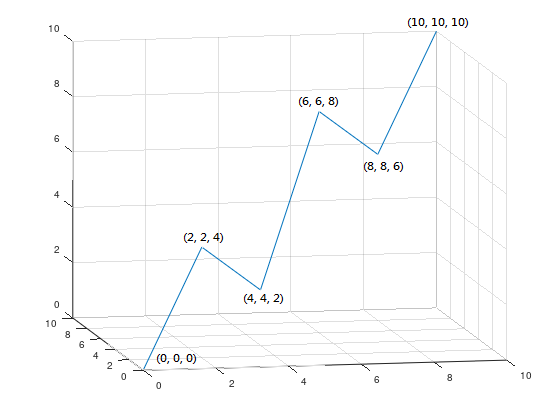
The path can be achieved using the following G-Code:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
|
Or use the line function directly:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
|
Arc motion:
When using the arc motion method to control Machine, you can use two different ways to control the arc path: 1. Center mode – that is, give the center and end point position to calculate the arc path. 2. Radius mode – that is, give the radius and end point position to calculate the arc path. 3. Radius mode – gives the radius to calculate the path of the arc. Regardless of which mode is used, you will need to select the clockwise and counterclockwise directions, as shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3:
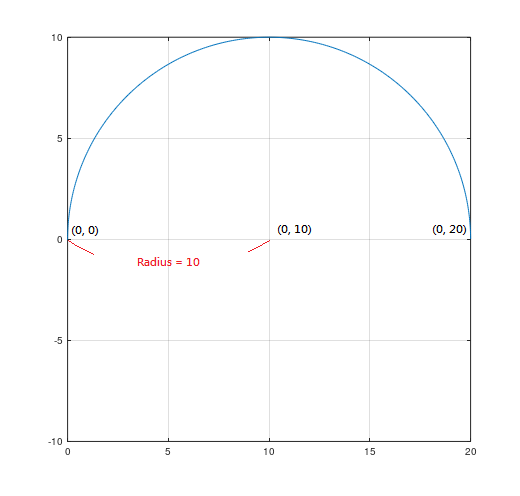
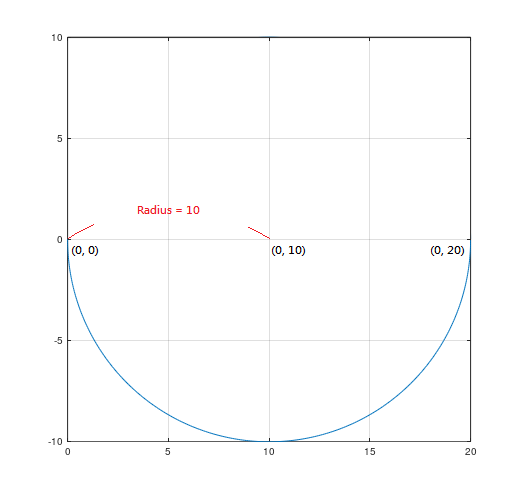
In G-Code, you can directly use G2 (CW) and G3 (CCW) as instructions to distinguish directions.
As shown in Figure 2, the following G-Code can be used to achieve it:
|
1 |
|
And Figure 3 can be achieved with the following G-Code:
|
1 |
|
Or use arcXY, arcYZ, arcXZ functions directly, as shown in Figure 2:
|
1 |
|
Figure 3:
|
1 |
|
When using radius mode, when the angle is not equal to 180 degrees, 4 different paths will be generated, as shown in Figure 4:
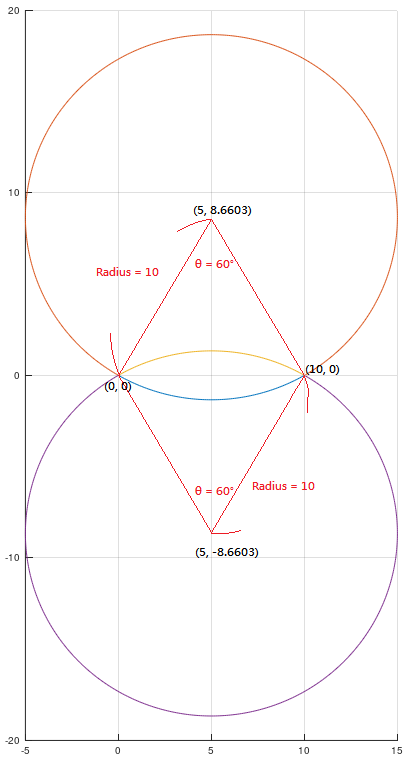
Figure 4
The radii of the four arcs above and below in Attached Figure 4 are all 10, and the target position is the same. Here, the positive and negative signs of the radius are used to determine the path.
If you want to select an arc with an angle less than 180 degrees, the radius is a positive value; if you want to select an arc with an angle greater than 180 degrees, the radius is a negative value.
If the yellow line in Figure 4 is clockwise and the angle of the arc is less than 180 degrees, the following G-Code can be used to achieve it:
|
1 |
|
Or directly use the multi-loaded methods of arcXY, arcYZ, and arcXZ functions:
|
1 |
|
The orange line is clockwise and the angle of the arc is greater than 180 degrees, can be achieved with the following G-Code:
|
1 |
|
Or directly use arcXY, arcYZ, arcXZ Function multi-load method:
|
1 |
|
The blue line is counterclockwise and the angle of the arc is less than 180 degrees. The following G-Code can be used to achieve it:
|
1 |
|
Or directly use the multi-loaded methods of arcXY, arcYZ, and arcXZ functions, and use the parameter revDir to control the direction:
|
1 |
|
The purple line is counterclockwise and the angle of the arc is greater than 180 degrees. The following G-Code can be used to achieve it:
|
1 |
|
Or directly use the multi-loaded methods of arcXY, arcYZ, and arcXZ functions, and use the parameter revDir to control the direction:
|
1 |
|
※Note that no matter which arc motion method is used, the target position may not be on the circle due to incorrect parameter settings, which will cause the machine to move unexpectedly.
In the radius mode, arcXY_Theta, arcXZ_Theta, arcYZ_Theta can be used directly to control the movement of the Machine, and the radius sign is used to determine the direction, as shown in the following example:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
|
Circular motion:
When the circular motion method is used to control the Machine, the machine will move in a circular motion to reach the target position:
When the current position of the arc motion overlaps with the target position, the Machine will regard it as a full circle.
If the G-Code parameter P is added, it can also indicate how many circles to make, as shown in the following example:
|
1 2 |
|
For counterclockwise movement, use G3, the same as arc movement.
Or you can directly use the circleXY, circleYZ, circleXZ functions to draw a circle to the current position, and use the parameter revDir to control the direction:
|
1 2 |
|
※ In the center and radius mode, when the origin and the target position are the same, there will be infinite combinations, in which case no movement will be made.
Spiral motion:
When the spiral motion method is used to control the machine, the machine will move the fire target position in a spiral motion on the XY, YZ, and XZ planes, as shown in Figures 5, 6, and 7:
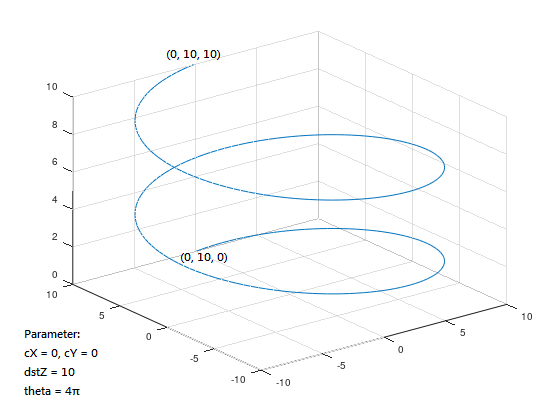
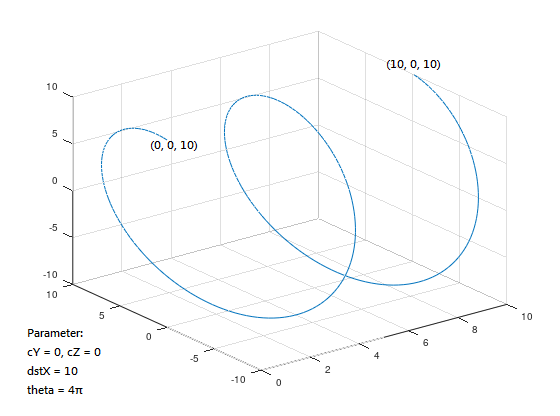
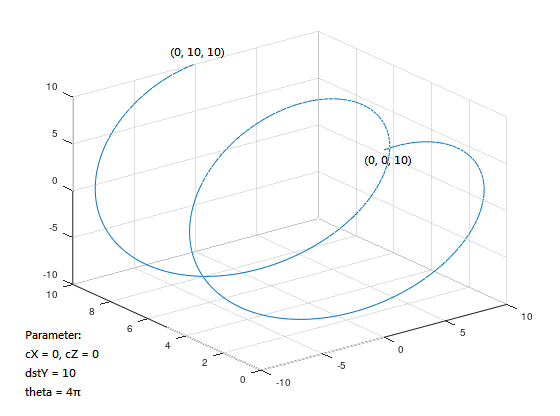
Spiral motion can directly use helicalXY, helicalYZ, and helicalXZ functions to determine the plane, and use the positive and negative signs of the radius to determine the direction:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
|
See Also
gcode()
arcXY()
arcXZ()
arcYZ()
arcXY_Theta()
arcXZ_Theta()
arcYZ_Theta()
circleXY()
circleXZ()
circleYZ()
helicalXY()
helicalXZ()
helicalYZ()
Library Reference
The text of the 86Duino reference material is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 License. The code examples in the reference material have been released into the public domain.
